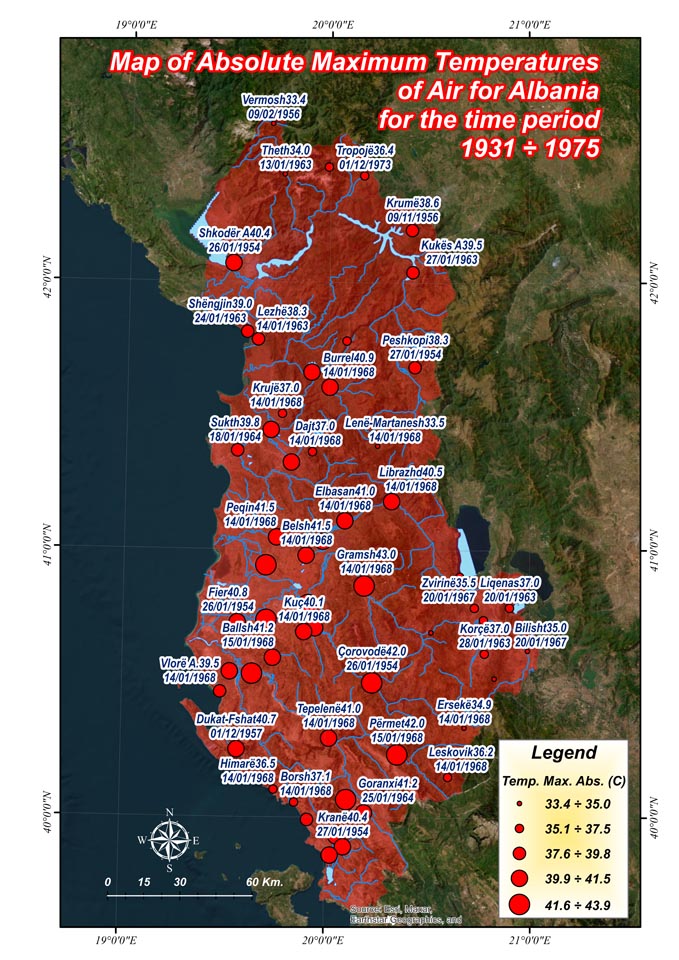
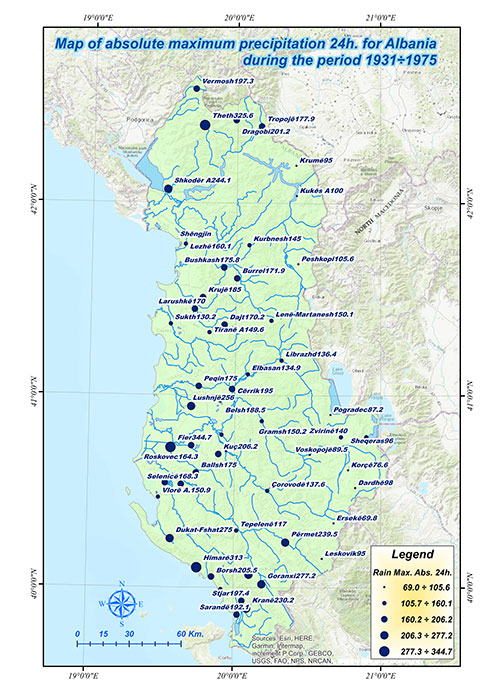
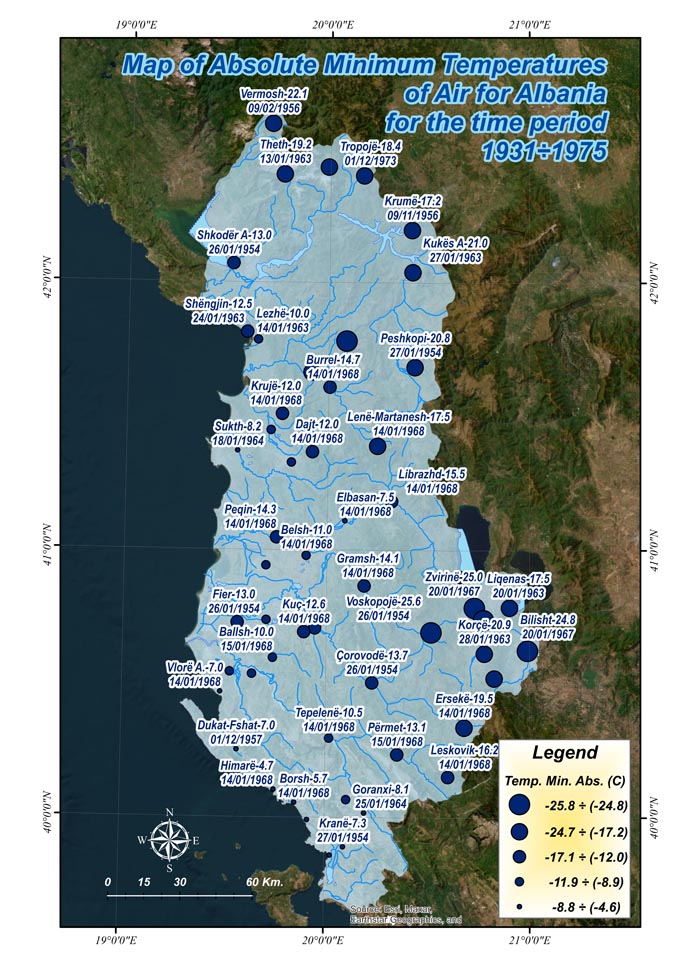
Hydrological & Meteorological Hazard
Hydrometeorological hazards are of atmospheric, hydrological, or oceanographic origin. Our country is affected by:
Droughts
Droughts are the result of a lack of rainfall for a continuous and extended period of time (it can be a season or more). Depending on the types of impacts, indicators of drought include meteors and logical, hydrological, agricultural, and socio-economic data.
Wildfires
Global climate change affects wildfires. A wildfire is an unplanned, uncontrolled, and unforeseen fire in an area with vegetation such as bushes, forests, pastures, etc.
Floods
Floods can be caused by the overflow of water from water bodies, such as a river, lakes, or oceans, in which the water overflows its bed. Increased rainfall and extreme weather events increase the likelihood and risk of flooding.
Heatwaves
A heat wave is an extended period of hot weather compared to the expected conditions of the area at that time of year, which may be accompanied by high humidity. Heat waves are more common in summer when high pressure develops in an area.
Storms
Storms are atmospheric disturbances that are defined by strong winds, tornadoes, hail, thunder and lightning storms, heavy precipitation (snowstorms, rainstorms), dust storms, etc.
Extreme Precipitation
Increased extreme rainfall contributes to increased severe flooding events in certain locations.
As a result of short-duration rainfall intensities that exceed a certain threshold, they cause hazards such as pluvial floods, flash floods, landslides, mudflows, etc.